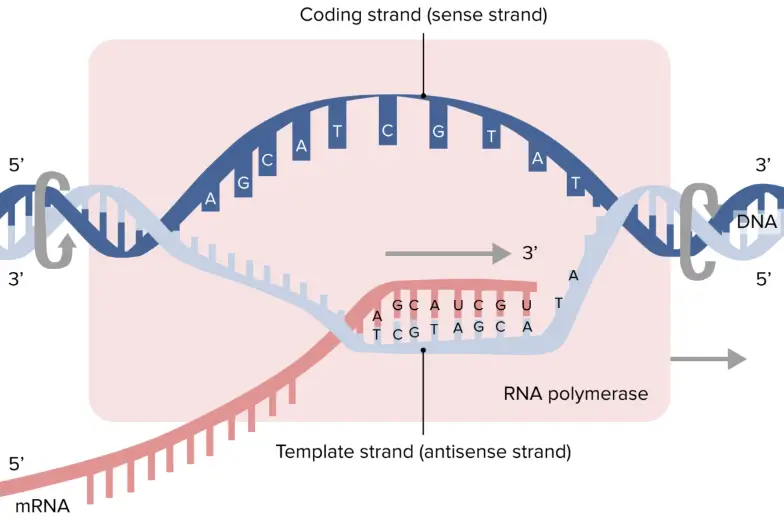
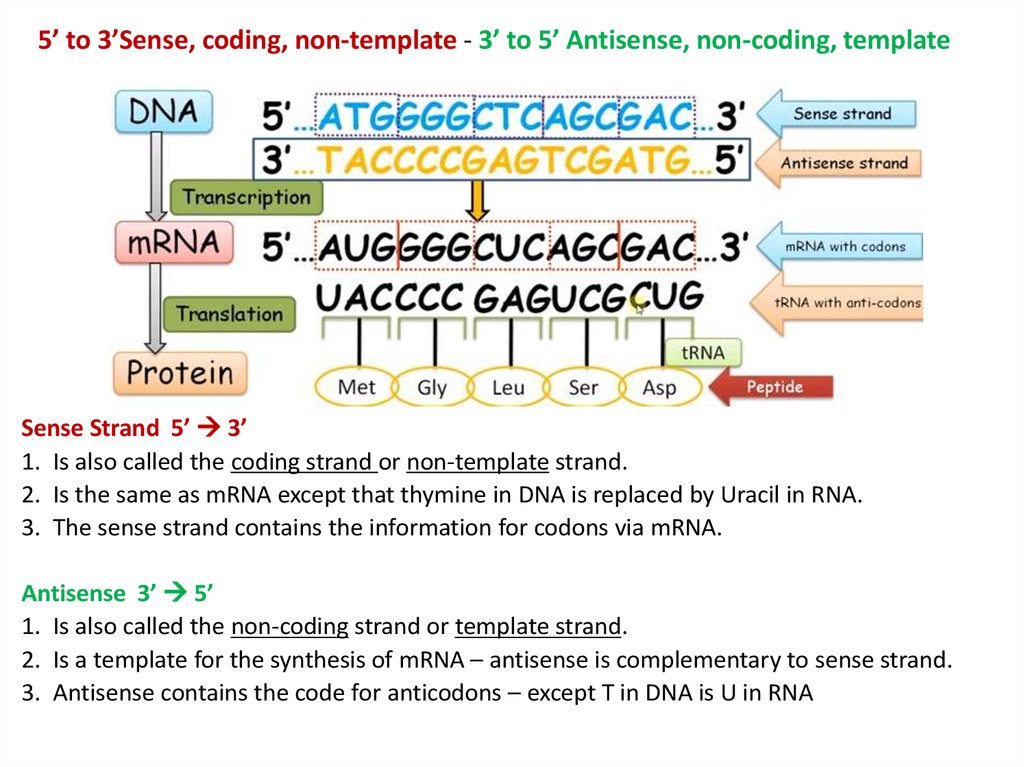
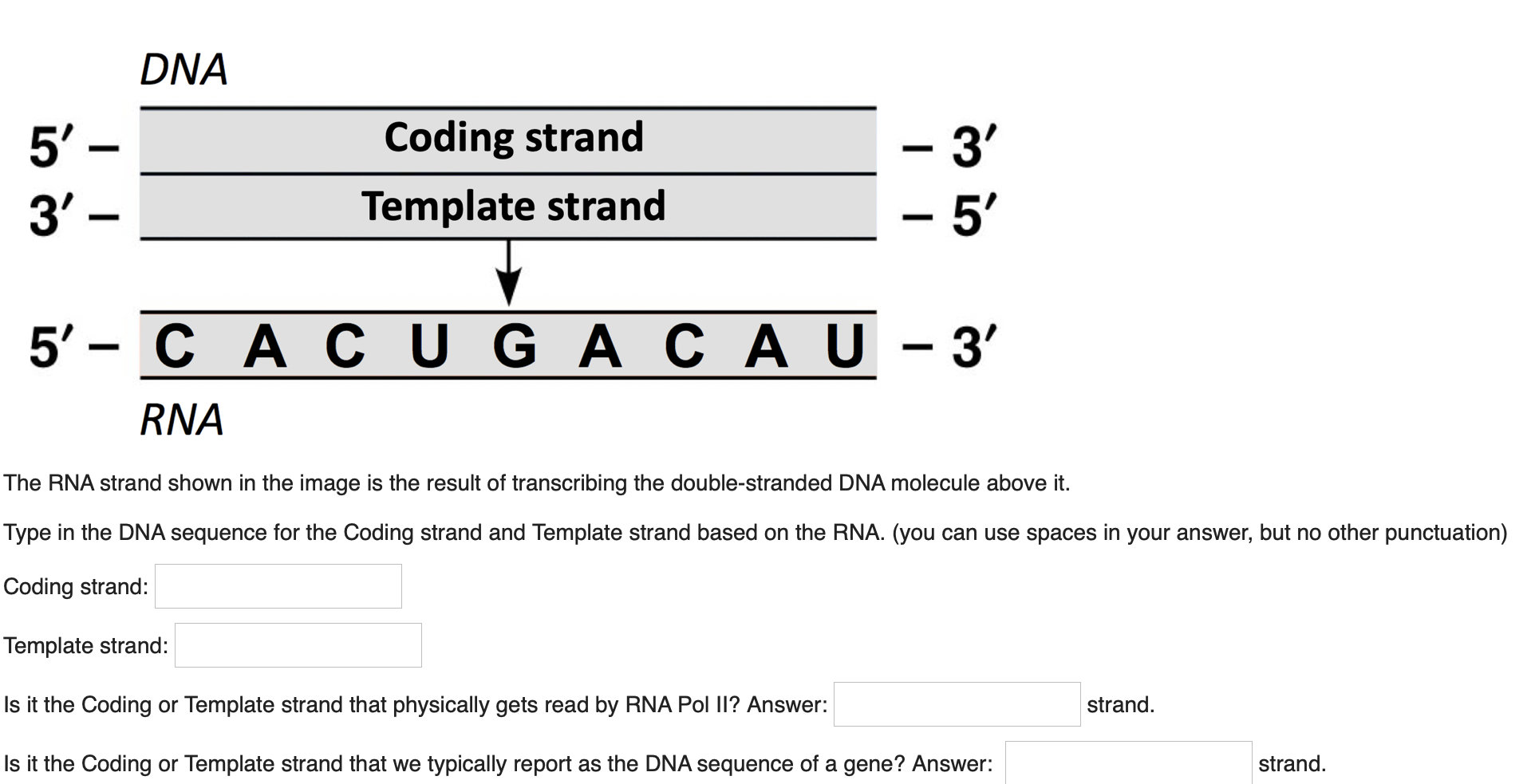
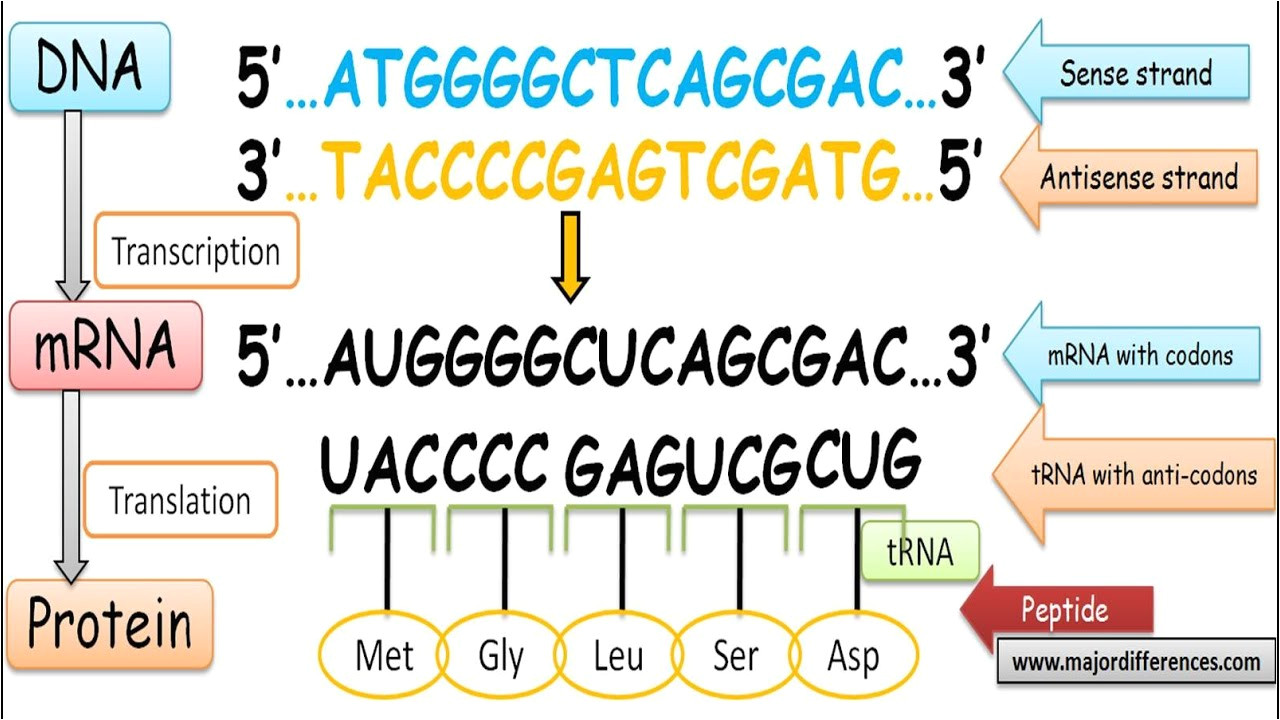
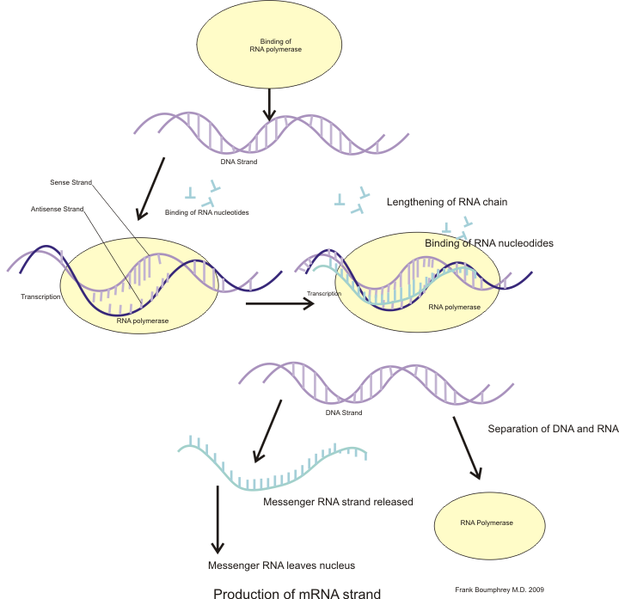
Coding And Template Strand
Coding And Template Strand - During the process of transcription, one of the two. The other strand of dna. Web template and coding strands are the terms generally used to describe the strands which are present in the dna. The mrna produced is consequently sense rna. Web the difference between a template and a coding strand is primarily based on two characteristics: Web in this mcat question of the day, we will be taking a look at the key differences between the template strand and the coding/sense strand. Web the coding strand is the template strand (it's also called the sense or transcribed strand). 4 given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that. Web overview of transcription transcription is the first step in gene expression, in which information from a gene is used to construct a functional product such as a protein. In most organisms, the strand of dna that. Web the coding strand turns gray and then disappears, leaving the template strand (see strands above ). The other strand of dna. Web overview of transcription transcription is the first step in gene expression, in which information from a gene is used to construct a functional product such as a protein. The dna strand that would correspond to. Web template. Web overview of transcription transcription is the first step in gene expression, in which information from a gene is used to construct a functional product such as a protein. Web the difference between a template and a coding strand is primarily based on two characteristics: In most organisms, the strand of dna that. Coding strand is also called a template. 4 given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that. The other strand of dna. Web the coding strand turns gray and then disappears, leaving the template strand (see strands above ). The dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint. Web 6. Web the coding strand is the dna strand which cannot act as a template and its base sequence is similar to its primary rna transcript. In most organisms, the strand of dna that. Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. Web the. Coding strand is also called a template strand which gets transcribed to rna. During the process of transcription, one of the two. Web 6 rows the coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. Web template and coding strands are the terms generally used to describe the strands which are present in the dna. Web in this mcat. Web 6 rows the coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. Coding strand is also called a template strand which gets transcribed to rna. Web the difference between a template and a coding strand is primarily based on two characteristics: The dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint. The other strand of dna. Web in this mcat question of the day, we will be taking a look at the key differences between the template strand and the coding/sense strand. The dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint. The other strand of dna. In most organisms, the strand of dna that. Web the coding strand is the dna strand which. Web the coding strand turns gray and then disappears, leaving the template strand (see strands above ). Web 3 answers sorted by: During the process of transcription, one of the two. Web the difference between a template and a coding strand is primarily based on two characteristics: Web in this mcat question of the day, we will be taking a. Web the coding strand is the dna strand which cannot act as a template and its base sequence is similar to its primary rna transcript. Web overview of transcription transcription is the first step in gene expression, in which information from a gene is used to construct a functional product such as a protein. In most organisms, the strand of. Web 3 answers sorted by: Web the coding strand is the dna strand which cannot act as a template and its base sequence is similar to its primary rna transcript. Web 6 rows the coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. During the process of transcription, one of the two. The dna strand that would correspond to. Web in this mcat question of the day, we will be taking a look at the key differences between the template strand and the coding/sense strand. Web the difference between a template and a coding strand is primarily based on two characteristics: Web 3 answers sorted by: Web the coding strand is the dna strand which cannot act as a template and its base sequence is similar to its primary rna transcript. Web the coding strand is the template strand (it's also called the sense or transcribed strand). Web the coding strand turns gray and then disappears, leaving the template strand (see strands above ). The two distinct strands of double. Web template and coding strands are the terms generally used to describe the strands which are present in the dna. The dna strand that would correspond to. Coding strand is also called a template strand which gets transcribed to rna. The mrna produced is consequently sense rna. Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. 4 given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that. In most organisms, the strand of dna that. The dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint. The other strand of dna. During the process of transcription, one of the two. Web 6 rows the coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. Web overview of transcription transcription is the first step in gene expression, in which information from a gene is used to construct a functional product such as a protein. The dna strand that would correspond to. Web 3 answers sorted by: 4 given a dna sequence alone, you can annotate open reading frames (orfs) in order to identify the coding strand, with the caveat that. The other strand of dna. Web the coding strand is the dna strand which cannot act as a template and its base sequence is similar to its primary rna transcript. Web 6 rows the coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. The dna strand known as the template strand serves as a blueprint. Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. Web the coding strand is the template strand (it's also called the sense or transcribed strand). Coding strand is also called a template strand which gets transcribed to rna. Web template and coding strands are the terms generally used to describe the strands which are present in the dna. Web in this mcat question of the day, we will be taking a look at the key differences between the template strand and the coding/sense strand. During the process of transcription, one of the two. Web overview of transcription transcription is the first step in gene expression, in which information from a gene is used to construct a functional product such as a protein. The mrna produced is consequently sense rna.DNA Transcription Steps and Mechanism • Microbe Online
Information Flow and Levels of Regulation Medical 1st Ed
Template Vs Nontemplate Strand
Coding Strand of DNA bartleby
Difference between template and coding strand Definition, properties
IMP Coding (Sense) vs Template (AntiSense) Strands Biology activity
Solved DNA 5' 3' Coding strand Template strand 3' 5'
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand williamsonga.us
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand Compare the Difference
The coding strand of DNA is 5'AATTCAAATTAGG3'
Web The Difference Between A Template And A Coding Strand Is Primarily Based On Two Characteristics:
The Two Distinct Strands Of Double.
Web The Coding Strand Turns Gray And Then Disappears, Leaving The Template Strand (See Strands Above ).
In Most Organisms, The Strand Of Dna That.
Related Post: